With 1~5-Years Staying History, How to Get Japanese Permanent Residency?
Those who can apply for “Permanent Residency” with less than 10-years staying history
CONTENTS
[Show/Hide]
- 1. Introduction
- 2. 10 years or longer continuous staying history is required for permission of permanent residency (“Continuous Stay Requirement”)
- 3. Those who can apply for “Permanent Residency” with less than 10-years continuous staying history
- ① Spouse or child of a Japanese national, special permanent resident or permanent resident
- ② A person with the status of “Long Term Resident”
- ③ A person recognized as a refugee
- ④ A person recognized to have made a contribution to Japan in specific fields
- ⑤ A person engaged in specific activities such as research, instruction, and information processing in specific fields
- ⑥ A person having a total score of 70 points or more based on the points calculation criteria for “Highly-Skilled foreign Professional”
- ⑦ A person having a total score of 80 points or more based on the points calculation criteria for “Highly-Skilled foreign Professional”
- 4. Summary
1. Introduction

As explained in the page of “Legal requirements of permission for “Permanent Residence” in Japan”, 10-years continuous staying history in Japan is required (“Continuous Stay Requirement”).
On the other hand, there are some exceptional cases in “Continuous Stay Requirement”, where foreign nationals can get the permission of permanent residency even if their continuous staying history is shorter than 10-years.
- Who can apply for “Permanent Residency” with less than 10 years continuous staying history?
- How long shall the continuous staying periods be in case the exception is applied?
=> Jump to the conclusion of this article

2. 10 years or longer continuous staying history is required for permission of permanent residency (“Continuous Stay Requirement”)
As mentioned above, foreign nations shall continuously stay in Japan for 10 years or longer to get the permission of permanent residency (“Continuous Stay Requirement”).
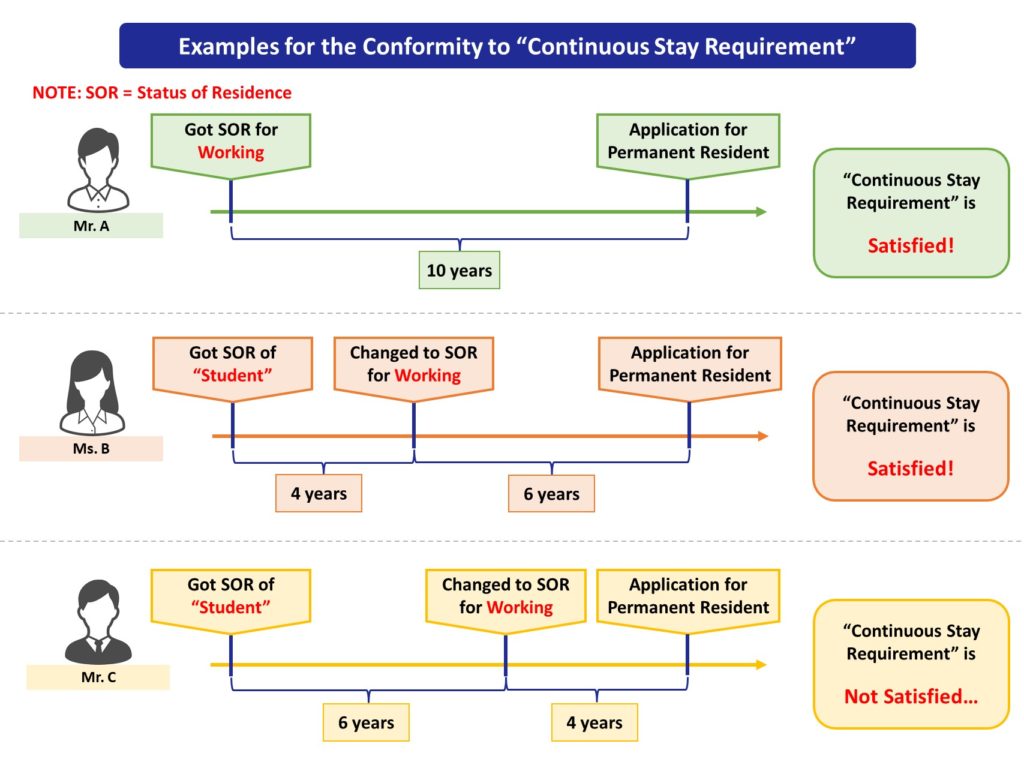
This image is what was used in the page of “Legal requirements of permission for “Permanent Residence” in Japan” to explain “Continuous Stay Requirement”.
Mr. A and Ms. B have continuously stayed in Japan to satisfy “Continuous Stay Requirement” so as to get the permission for application of permanent residency.
- Mr. A:
Continuously stayed in Japan for 10 years after getting the status for working, then applied for permission of permanent residency. - Ms. B:
Continuously stayed in Japan for 4 years with the status of “Student” and for 6 years with the status for working (total 10 years), then applied for permission of permanent residency.
In principle, it takes 10 years long time to get the permission of permanent residency, however, there are some exceptional cases where the continuous staying history shorter than 10 years is set for “Continuous Stay Requirement”.
The details of such exceptional cases are explained in the next chapter.

3. Those who can apply for “Permanent Residency” with less than 10-years continuous staying history
There are 7 exceptional cases where continuous staying history shorter than 10 years is set as “Continuous Stay Requirement”.
The foreign nationals who fall under any one of the 7 exceptional cases can be recognized to satisfy “Continuous Stay Requirement” by continuously staying in Japan for the period mentioned in each exceptional case.
① Spouse or child of a Japanese national, special permanent resident or permanent resident

- Spouse of Japanese, permanent resident, or special permanent resident
To have been in a real material relationship for more than 3 years consecutively and have stayed in Japan more than 1 year consecutively. - True child of Japanese, permanent resident, or special permanent resident
To have stayed in Japan for more than 1 year consecutively.
Extra Info.
The abovementioned “Spouse” and “True child” of Japanese, permanent resident, or special permanent resident do NOT stand for the status of residence.
Therefore, the applicant who is PRACTICALLY spouse or real child of Japanese, permanent resident, or special permanent resident can be recognized to fall under this exceptional case.
In this case, it is NOT required to have the status of “spouse or real child of Japanese, permanent resident, or special permanent resident”.
② A person with the status of “Long Term Resident”
To have stayed in Japan for more than 5 years consecutively with the status of “Long Term Resident”.
③ A person recognized as a refugee
To have stayed in Japan for more than 5 years consecutively after recognition.
④ A person recognized to have made a contribution to Japan in specific fields

To be recognized to have made a contribution to Japan in the fields including diplomatic, social, economic, cultural fields, and to have stayed in Japan for more than 5 years.
Extra Info.
Those who fall under this exceptional case are, for example, following persons:
・winner of Novel Prize;
・person who is engaged in the management of Japanese company and has contributed to the development the economy;
・winner of authoritative prize in the field of art; and
・higher-ranking winner of Olympic or other competitions.
⑤ A person engaged in specific activities such as research, instruction, and information processing in specific fields
To have stayed in Japan for more than 3 years consecutively; and
to be recognized to have made a contribution to Japan through the activities such as research, instruction, and information processing in the public or private institutions located in the area of the plan specified in the regional revitalization plan.
⑥ A person having a total score of 70 points or more based on the points calculation criteria for “Highly-Skilled foreign Professional”

- a: To have stayed in Japan for more than 3 years consecutively as a “Highly-Skilled Foreign Professional”.
- b: To have stayed in Japan for more than 3 years consecutively, and to be deemed to have a total of 70 points ore more when calculating with reference to the situation at 3 years before the date of the application for permission fore permanent residence.
Extra Info.
“Point” is calculated based on the “Points Calculation Table” issued by Immigration Services Agency of Japan. The point is used to evaluate the skill of foreign nation as a professional.
The foreign nationals with the predetermined points or more can accept some preferential treatments in some immigration procedures.
– Examples of Preferential Treatment –
・Exception of “10-years continuous residence in Japan” on permanent residence application
・Working permission of spouse
・No regulation on the staying period
External Link: Points Calculation Table
⑦ A person having a total score of 80 points or more based on the points calculation criteria for “Highly-Skilled foreign Professional”
- a: To have stayed in Japan for more than 1 year consecutively as a “Highly-Skilled Foreign Professional”.
- b: To have stayed in Japan for more than 1 year consecutively, and to be deemed to have a total of 80 points ore more when calculating with reference to the situation at 3 years before the date of the application for permission fore permanent residence.

4. Summary
- Who can apply for “Permanent Residency” with less than 10 years continuous staying history?
➊ Spouse or child of a Japanese national, special permanent resident or permanent resident
➋ A person with the status of “Long Term Resident”
➌ A person recognized as a refugee
➍ A person recognized to have made a contribution to Japan in specific fields
➎ A person engaged in specific activities such as research, instruction, and information processing in specific fields
➏ A person having a total score of 70 points or more based on the points calculation criteria for “Highly-Skilled foreign Professional”
➐ A person having a total score of 80 points or more based on the points calculation criteria for “Highly-Skilled foreign Professional” - How long shall the continuous staying periods be in case the exception is applied?
➊ 1 year or longer
➋ 5 years or longer
➌ 5 years or longer
➍ 5 years or longer
➎ 3 years or longer
➏ 3 years or longer
➐ 1 year or longer
If you have some questions or points to be more deeply explained, please feel free to ask us through the contact form!
Japanese Immigration Column
Columns on Japanese immigration, visa, naturalization, and diplomatic affairs.
- Japan to Accept Over 100,000 Foreign StudentsJapan is accelerating acceptance of foreigners, especially foreign students. 150,000 foreign students are waiting to enter Japan, and 100,000 of them are forecasted to enter Japan until end of May 2022.
- Japan Government to Change Upper Limit of Entrance to 10,000/day from April 10On April 1, 2022, Japan Chief Cabinet Secretary Hirokazu Matsuno declared that Japanese government will loose the entrance regulation to change the upper limit from 7,000/day to 10,000/day from April 10.
- Japan Government to Provide Life Support Money and Place for Residence, Chief Cabinet Secretary SaidOn April 1, 2022, Japanese Government held the conference for discussing the acceptance of Ukraine refugees.
- Yokohama-city, Japan, to accept Ukraine RefugeesOn Mar. 8, 2022, Mayor of Yokohama-city, Kanagawa Pref., Japan, declared that Yokohama-city prepared approximately 80 municipal housings for Ukraine refugees.
- Japanese Special Measure “COE Extension” due to Omicron VariantOn Dec. 28, 2021, Immigration Services Agency of Japan has declared the special extension of COE validity due to the impact of omicron variant.
- Sanction “Suspension of Visa Issuance”, Japanese Prime Minister Kishida has announcedOn Feb. 23, 2022, Japanese Prime minister Kishida Fumio announced the sanctions on Russia. The sanctions include the suspension of visa issuance against Russian citizens.
- Japan to increase number of entry up to 7,000/day, Kishida declaredOn Mar. 3, 2022, Japanese Prime Minister Kishida declared that Japan will loosen the regulation of entry of foreigners from 5,000 to 7,000/day.






