Guideline for changing VISA (status of residence) in Japan
Documents / Legal requirements / Timing to apply
CONTENTS
[Show/Hide]
- Introduction
- What is “Application for Change of Status of Residence”?
- General Flow of Application for Change of Status of Residence
- Legal Requirements of Application for Permission of Change of Status of Residence
- Required Documents for Application for Change of Status of Residence
- Example cases where change of status of residence is necessary
- Standard Period of Time for Procedure
- Timing of Application
- Penalty
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Q. Where do I have to submit the application documents for change of status of residence?
- Q. Must foreign student change status of residence to engage in part-time job?
- Q. Is online application available?
- Q. How much is the fee for change of status of residence?
- Q. I will marry Japanese national. Must I change my status of residence to “Spouse or Child of Japanese National”?
- Summary
Introduction
As explained in the page of “Status of residence in Japan” (ENG. ver. coming soon!), every non-Japanese national is given a status of residence when he/she enters Japan. Non-Japanese must do the activity the contents of which suit the given status of residence while staying in Japan.
Change of status of residence is the procedure necessary to do the activities that are NOT allowed to the current status of residence.
In case non-Japanese national dose the activities that are NOT allowed to his/her current status of residence, penalty will apply.
- What is Application for Change of Status of Residence?
- General flow of Application for Change of Status of Residence
- 3 legal requirements for Change of Status of Residence
- Application documents according to respective status of residences
- Period of time for examination
- Timing to make application
- Penalty
=> Jump to the conclusion of this article

What is “Application for Change of Status of Residence”?
Change of status of residence is the procedure necessary to do the activities that are NOT allowed to the current status of residence.
For example, it is required in the following cases:
- Non-Japanese national staying in Japan with the status of “Engineer/Specialist in Humanities/International Services” marries a Japanese, and changes the status to “Spouse or child of Japanese national”
- Non-Japanese national staying in Japan with the status of “Student” changes the status to “Engineer/Specialist in Humanities/International Services” to join a company located in Japan
Like the above example cases, when the occupation changes or non-Japanese national marries Japanese/permanent resident, status of residence must be changed too.

General Flow of Application for Change of Status of Residence
Flow of application for change of status of residence is generally as follows.
- STEP1. Preparation and collection of application documents
- Firstly, documents required for the application have to be prepared and collected.
It is recommended to start preparation and collection as early as possible because some documents have to be issued by public office, company, or school. Issuance of those documents sometimes takes longer time than applicator’s expectation.
- STEP2. Filling of application documents
- Submit the prepared/collected documents to Immigration Services Agency of Japan.
Please refer to FAQ. “Where do I have to submit the documents for application for change of status of residence?” to know the location of local office of Immigration Services Agency of Japan for your residence area.
- STEP3. Examination
- Immigration Services Agency of Japan stars examination of the application based on the submitted documents.
The period of time for examination is about 2 weeks to 1 month.
Sometimes, additional documents are required by the Agency during the examination. In this case, it is highly recommended to submit the required documents as early as possible.
- STEP4. Result notification from the Agency
- Postcard for the result notification of the application is sent from the Agency.
In case of denial of the application, postcard notifying the denial is sent to the applicator.
- STEP5. Reception of renewed resident card
- Applicator has to go to local office of Immigration Services Agency of Japan to receive the renewed resident card.
The renewed resident card is given to the applicator in exchange for the postcard.

Legal Requirements of Application for Permission of Change of Status of Residence
There are 3 legal requirements to get the permission of change of status of residence as follows.
Requirements ① and ② must be satisfied regardless of the current status of residence.
On the other hand, requirement ③ must be satisfied only when the current status of residence is “Temporary Visitor”.
① Conformance with the New Status of Residence
Conformance with the status of residence is defined in Immigration Control and Refugee Recognition Act Article7 paragraph1 item(ii) as follows.
Conformance with the Status of Residence
the activities stated in the application to be conducted while in Japan (…) fall under either of
Immigration Control and Refugee Recognition Act Article7 paragraph1 item(ii)
➊ the activities set forth in the right-hand column of the Appended Table I (…) or
➋ the activities of a person with a status or position set forth in the right-hand column of the Appended Table II (…).
* partially abbreviated and edited for easy understanding
Based on above clause, conformance with the new status of residence can be explained as follows:
The activity (status) that the applicant wants to do (get) suits any one of the statuses of residence listed in the Immigration Control and Refugee Recognition Act.
For more detail on the conformance with the status of residence, please refer to the following related post.
② Good conduct during staying in Japan (“狭義の相当性” in Japanese)
This requirement can be explained as follows:
Applicant’s conducts and status of activity is suitable enough to give the permission of change of status of residence.
Some major items to measure applicant’s conformance with this requirement is listed in “Guidelines for Permission for Change of Status of Residence and Extension of Period of Stay” issued by Immigration Services Agency as follows.
- Applicants must have engaged in activities that are in accordance with the current status of residence.
For example, a technical intern trainee who has absconded or an foreign student who has stayed in Japan after being expelled from or leaving school and engaged in activities not in accordance with their status of residence is evaluated negatively except in cases where there is a justifiable reason for doing so. - Applicants must have good behavior.
Specifically, those who have committed any act subject to criminal punishment that falls under any reason for deportation or act that cannot be overlooked in terms of immigration services administration, including mediation of illegal work, will be considered to exhibit bad behavior. - Applicants must have sufficient assets or ability to make an independent living.
An applicant’s living situation must not be a burden to the public and the applicant must have the possibility of continuing to live a stable life in the future, considering his/her assets or ability (both on a personal basis and on a household basis).
However, even in the case where an applicant’s living situation is a burden to the public, when there are humanitarian reasons to grant permission to stay in Japan, the decision will be made giving due consideration to such reasons. - Proper employment and working conditions must be met.
In the case of applicants who (intend to) get a job in Japan, including a part-time job, their employment and working conditions must comply with labor-related laws. - Tax obligations must be fulfilled.
A failure to fulfill their obligation will be recognized as a negative element. For example, those who have been punished for non-fulfillment of tax payment obligations will be considered to have failed to fulfill their tax payment obligations.
Even in the case of those who have not been punished, when it is found that they have not paid a high amount of tax or that they have not paid tax for a long time, and when such acts are considered malicious, they will be treated the same as those who have been punished - Obligations provided by the Immigration Control Act, including notification obligations, must be fulfilled.
Foreign nationals who lives in Japan must fulfill the obligations set forth in Immigration Control Act including notification of the matters described on the residence card, application for renewal of validity of the residence card, application for re-issuance of the residence card due to loss etc., return of the residence card, and notification of the organization to which they belong.
Extra Info.
The above items are examples that Immigration Services Agency publishes.
Therefore, applicant may be considered NOT to satisfy Requirement② even if all the above items are satisfied.
③ The application is made based on special unavoidable circumstances.
As mentioned above, this requirement must be satisfied only when the current status of residence is “Temporary Visitor”.
Following cases are the typical examples where this requirement may be considered to be satisfied when:
- application is for changing the status to “Spouse or Child of Japanese National” or “Spouse or Child of Permanent Resident” due to marriage;
- applicant is a child of Japanese national or permanent resident;
- applicant is a spouse, child or biological parent of Highly Skilled Professional, or parent of Highly Skilled Professional’s spouse;
- applicant with the status of “Temporary Visitor” gets certificate of eligibility (COE) of another status of residence during his/her stay in Japan;
- it is difficult for applicant with the status of “Temporary Visitor” to go back to his/her country due to sickness or injury; and
- applicant with the status of “Temporary Visitor” passes the entrance examination of university or some other school, and the course will start within about 1 month from the end of the period of stay.
Extra Info.
In addition to the above requirements①~③, conformity with the landing permission criteria is taken into consideration in the examination of application for permission of change of status of residence.
Related Post: Conformity to Status of Residence and Landing Permission Criteria (ENG. ver. coming soon!)

Required Documents for Application for Change of Status of Residence
Required documents for application for change of status of residence differ in accordance with the status of residence that applicant want to get.
In this article, we introduce the required documents for the following major statuses of residence.
- Engineer/Specialist in Humanities/International Services
- Student
- Spouse of Japanese National (when applicant is wife or husband of Japanese)
- Spouse of Permanent Resident (when applicant is wife or husband of permanent resident)
Required documents for “Engineer/Specialist in Humanities/International Services”
- Application form
- Photo of applicant
- Passport and residence card (only present, not submit)
- Documents certifying that the applicant falls under one of the categories 1 to 4
Category 1:
・Copy of a quarterly report or another document proving that the company is listed on a Japanese stock exchange
・Copy of a document certifying that the institution has been approved by the relevant authorities
・Proof that the company is an “innovation company”
Category 2:
・Copy of the total statutory report, including withheld taxes for earned income from the previous year (stamped with the seal of the office that accepted it)
・Documents proving that the institution has received approval to use the online residency application system (emailed notices of approval, etc.)
Category 3:
・Copy of the total statutory report, including withheld taxes for earned income from the previous year (stamped with the seal of the office that accepted it) - Document proving that the applicant has graduated from a professional training college and obtained the appropriate title(s) for their respective field (if applicants has obtained such title(s))
- Document certifying the activities that applicant will conduct in the work place (in case the applicant will work based on the dispatch worker contract)
In addition to the above documents, the following documents are required when the category of the institute is 3 or 4.
- One of the following documents that clearly defines the activities of the applicant:
(1) In cases where a labor contract is being executed:
Documents which state that the working conditions are compliant with Article 15, Paragraph 1 of the Labor Standards Act, and Article 5 of the Ordinance for the Enforcement of the Labor Standards Act
(2) In cases where the applicant is assuming a post as an executive member of a Japanese company:
Copies of either the articles of incorporation which detail the remuneration for executive members, or the minutes from the general shareholders meeting in which the remuneration was decided upon (for companies with a compensation committee, then those minutes)
(3)In cases where the applicant is transferring to the Japanese branch of a foreign company, or assuming a post as an executive member of a Japanese non-corporate organization:
Documents from the relevant organization which state the applicant’s position (job description), contract period, and remuneration - Document certifying the applicant’s academic background, work history, and other relevant background information:
(1) Resume which clearly outlines the applicant’s skills, knowledge, and period of time in which they have been employed in their field
(2) One of the following documents which prove the applicant’s academic background, work history, and other matters:
a: Either a university diploma or a certificate proving that the applicant has completed the equivalent (or higher) degree of post-secondary education; for those with DOEACC accreditation, proof of having obtained either Level A, B, or C
b: A Certificate of Employment or similar document which outlines the length of time the applicant has spend in the field (including certificates from universities, professional training colleges, or vocational schools which outline the time spent acquiring the necessary skills/knowledge
c: For IT engineers, proof of having obtained accreditation for or having passed an examination related to information processing technology, as determined in a special public notice made by the Minister of Justice
d: For those wishing to engage in activities which require an understanding of or sensitivity to foreign cultures, proof of a minimum of 3 years experience in the field (excluding those who majored in translation, interpretation or language education). - Certificate of registration
- One of the following documents that clearly defines the employment activities:
(1) Informative materials outlining the employer’s history, staff, structure, and business operations (including major clients and accomplishments)
(2) Other documents required to support/supplement the information provided above in point (1)
In addition to the above documents, the following documents are required when the category of the institute is 3.
- Recent financial documents (for the current fiscal year)
In addition to the above documents, the following documents are required when the category of the institute is 4.
- Copies of recent financial documents (for the current fiscal year), or copies of financial plans (for new businesses)
- Any of the following materials which clearly explain why the total statutory report (including withholding tax slips) from the previous year cannot be submitted:
(1) For institutions that do not need to withhold taxes at the source:
A certificate from a foreign corporation which proves that taxes do not need to be withheld at the source (or a similar document)
(2) For institutions other than the above in point (1):
1: Notification of the establishment of a payroll office, etc.
2: Either of the following materials:
a: Statements (copies of dated receipts) which show that income taxes (for retirement, etc.) have been paid over the past three months
b: Documents which show that approval has been obtained for an exemption of payment
Required documents for “Student”
- Application form
- Photo of applicant
- Passport, and residence card or certificate of alien registration (only present, not submit)
- Letter of financial support (in case other person pays expenses on behalf of the applicant)
⇒ Reference form (Japanese)
In addition to the above documents, applicant must submit some documents in accordance with the type of the institution the applicant is looking to receive education.
The list of such documents are available in the following web pages of Immigration Services Agency of Japan.
(1) University (including junior college and graduate school), institution equivalent to university, or technical school
a: Appropriate institution certified by Immigration Services Agency (Japanese)
b: Institution not certified by Immigration Services Agency (Japanese)
(2) Specialized Training College, Miscellaneous School, or institution that has facility and organization equivalent to Miscellaneous School (except for the institutions exclusively for Japanese language education)
a: Appropriate institution certified by Immigration Services Agency (Japanese)
b: Institution not certified by Immigration Services Agency (Japanese)
(3) Institution for Japanese language education and institution for preparatory education
a: Appropriate institution certified by Immigration Services Agency (Japanese)
b: Institution not certified by Immigration Services Agency (Japanese)
(4) Highschool, Junior Highschool, or Elementary School (Japanese)
Required documents for “Spouse of Japanese National” (when applicant is wife or husband of Japanese)
- Application form
- Photo of applicant
- Family register of the Japanese national (certificate of all items)
- Marriage certificate issued by an institution in the applicant’s home country (foreign country)
* If the applicant is listed in a family register in the Republic of Korea, then a copy of the foreign family register (which clearly defines the marriage between the two parties) is also permissible. - Documents proving the cost of one’s stay in Japan
(1) Tax certificate (or tax exemption certificate) for individual inhabitant taxes and a tax payment certificate for the most recent year (showing gross income and taxes paid for one year) for the person providing the applicant’s living expenses
(2) Other (when living expanses cannot be certified with the materials in (1)due to a recent arrival in Japan or moving)
a: Bankbook copies
b: Certificate of expected employment or a written job offer (issued by a Japanese company)
c: Equivalent of above - Spouse’s (Japanese national’s) guarantor form
⇒ Guarantor form (PDF, Japanese)
* The guarantor is the applicant’s Japanese spouse who resides in Japan. - Residence certificate of the Japanese spouse (which lists every member of household)
- Questionnaire form
⇒ Questionnaire form (PDF, Japanese) - Two or three candid photographs. (Both parties must be in each photograph, their faces clearly visible. Photographs which have been edited will not be accepted.)
- Passport (only present, not submit)
- residence card or certificate of alien registration (only present, not submit)
Required documents for “Spouse of Permanent Resident” (when applicant is wife or husband of permanent resident)
- Application form
- Photo of applicant
- Marriage certificate issued by an institution in either the spouse’s (permanent resident’s) or the applicant’s home countries (foreign countries)
* If the applicant is listed in a family register in the Republic of Korea, then a copy of the foreign family register (which clearly defines the marriage between the two parties) is also permissible.
* If the marriage was registered with a Japanese government office, then please present the notification of marriage. - Documents proving the cost of one’s stay in Japan
(1) Tax certificate (or tax exemption certificate) for individual inhabitant taxes and a tax payment certificate for the most recent year (showing gross income and taxes paid for one year) for the person providing the applicant’s living expenses
(2) Other (when living expanses cannot be certified with the materials in (1)due to a recent arrival in Japan or moving)
a: Bankbook copies
b: Certificate of expected employment or a written job offer (issued by a Japanese company)
c: Equivalent of above - Spouse’s (permanent resident’s) guarantor form
⇒ Guarantor form (PDF, Japanese) - Residence certificate of spouse (permanent resident) which lists every member of household
- Questionnaire form
⇒ Questionnaire form (PDF, Japanese) - Two or three candid photographs. (Both parties must be in each photograph, their faces clearly visible. Photographs which have been edited will not be accepted.)
- Passport (only present, not submit)
- Presentation of residence card or certificate of alien registration
Extra Info.
Other documents not listed above might be requested in the middle of the examination.
Example cases where change of status of residence is necessary
- When foreign student (foreign national with the status of “Student”) joins a Japanese company.
- When foreign national with the status of “Designated Activities” is looking to conduct the activity that is permitted to another “Designated Activities”.
- When foreign national with the status of “Spouse or Child of Japanese National/Permanent Resident” divorces Japanese/permanent resident.
- When foreign national with the status of “Engineer/Specialist in Humanities/International Services” who works for a Japanese company leaves the company, then founds his/her own company in Japan.
* In this case, the foreign national has to change the status to “Business Manager”.
Extra Info.
“Designated Activities” is defined in Immigration Control Act Appendix table I-(5) as follows:
“Activities which are specifically designated by the Minister of Justice for individual foreign nationals”.
In other words, even if 2 foreign nationals have the status of “Designated Activities”, the activities permitted to them can be different each other.
Therefore,foreign national has to change his/her status from “Designated Activities” to “Designated Activities” when he/she is looking to start another activity that is different from originally permitted one.
For the list of the activities permitted under the status of “Designated Activities”, please refer to the following page.
External Link: Immigration Services Agency of Japan / Notification by Ministry of Justice: Activities permitted to the status of “Designated Activities” (Japanese only)

Standard Period of Time for Procedure
Standard period of time for procedure is 2 weeks to 1 month.
“Standard period of time for procedure” is the period that the authority generally takes until it gives some action to application.
This period is just standard, in other words, actual examination procedure can take longer than 1 month.

Timing of Application
Application for change of status of residence must be made after the reason for change is fixed.
Following situations are the examples of the timings when the reason for change is fixed.
- When foreign student gets a notice of offer from Japanese company through job hunting.
- When foreign national, with a status of residence for working, who works for Japanese company gets a notice of offer from another Japanese company through new-job hunting.
- When foreign national who is a spouse of Japanese national or permanent resident divorces.
Generally, application for change of status of residence is accepted only when remaining period of time until the start of employment contract or entry to school is about 3 months or less.
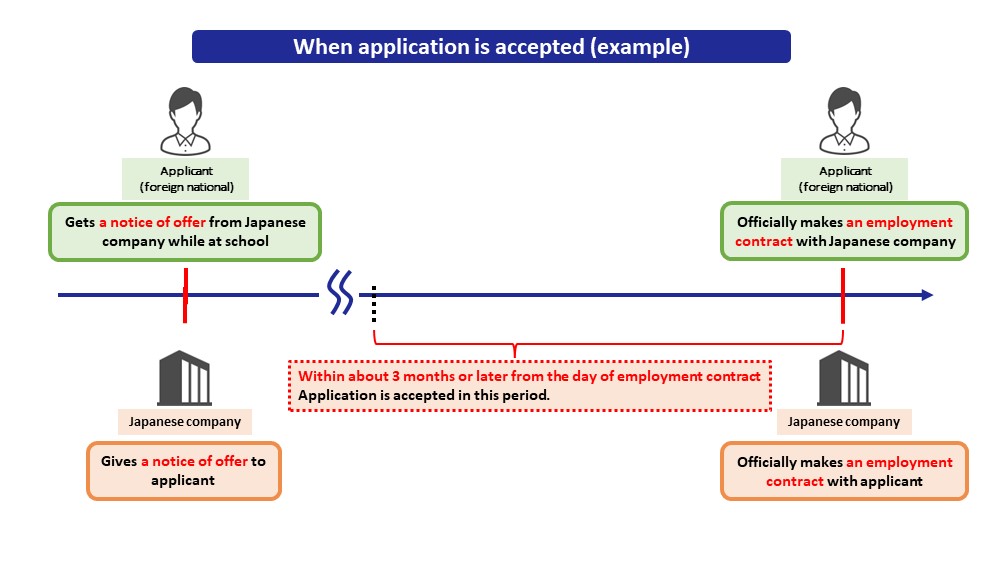
Extra Info.
Application of permission for extension of period of stay is accepted when remaining period of stay is about 3 months or less.
Related Post: Application for Extension of Period of Stay (ENG. ver. coming soon!)

Penalty
To engage in the activities that are NOT permitted to one’s current status of residence without changing to the proper status of residence is prohibited by Immigration Control Act Article 19.
Article 19 Scope of Activities
(1) Any foreign national who is a resident under a status of residence set forth in the left-hand column of the Appended Table I must not engage in the activities set forth in the following items in accordance with the categories identified therein (…):
item(i):
Immigration Control and Refugee Recognition Act Article19 paragraph1 item(i)
– (…) activities of managing a business involving income not included in those activities set forth in the right-hand column of those tables in accordance with the status of residence (NOTE: = the activities that are permitted to the current status of residence) or
– activities for which they receive remuneration (…)
* partially abbreviated and edited for easy understanding
When foreign national violates the above clause, the following penalties will be applied in accordance with the time used for prohibited activities and the continuity of violation.
When a foreign national is CLEARLY found to be engaged SOLELY in working activities that are not permitted to the current status of residence
In this case, following penalty is applied because of the violation set forth in Immigration Control Act Article70 paragraph(1) item(iv):
– Imprisonment with or without work for not more than 3 years,
– a fine not exceeding 3 million yen, or
– the cumulative imposition of imprisonment with or without work and a fine
Additionally, who falls under this case also falls under Immigration Control Act Article24 paragraph(1) item(iv) (a), thus he/she may be deported from Japan.
When a foreign national is found to be engaged in working activities that are not permitted to the current status of residence
In this case, following penalty is applied because of the violation set forth in Immigration Control Act Article73:
– Imprisonment with or without work for not more than 1 year,
– a fine not exceeding 2 million yen, or
– the cumulative imposition of imprisonment with or without work and a fine
Additionally, who falls under this case also falls under Immigration Control Act Article24 paragraph(1) item(iv) (f), thus he/she may be deported from Japan.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q. Where do I have to submit the application documents for change of status of residence?
A. Local office of Immigration Services Agency that controls applicant’s residence area.
You can check the locations of the local offices of Immigration Services Agency in the following page.
External Link: Regional Immigration Services Bureaus
Q. Must foreign student change status of residence to engage in part-time job?
A. No, however, “Permission to engage in activities other than permitted under the status of residence” is necessary.
When foreign student engages in part-time job without above permission, it is illegal working and thus penalty would be applied. You can check the detail of the permission for engaging in the activities that are not permitted to the current status of residence.
Q. Is online application available?
A. Online application is available.
However, it is available only in Japan. This is because IP addresses out of Japan are regulated to access the WEB page of online application.
You can access the online application page through the following link.
External Link: Immigration Services Agency of Japan / Online Application System
Q. How much is the fee for change of status of residence?
A. You have to pay JPY4,000 only when the application is permitted.
The fee must be paid with revenue stamp. Revenue stamp is available at the store located in Immigration Services Agency, however, it is normally crowded. Thus, to buy at post office or convenience store is recommended.
Q. I will marry Japanese national. Must I change my status of residence to “Spouse or Child of Japanese National”?
A. You can continue to stay in Japan without changing the status of residence.
For example, even if foreign national with the status of “Engineer/Specialist in Humanities/International Services” does not change his/her status of residence to “Spouse or Child of Japanese National” after he/she marries Japanese national, penalty would not be applied.
However, in that case, it is recommended to change the status of residence to “Spouse or Child of Japanese National”.
This is because those who has family related status of residence such as “Spouse or Child of Japanese National” can engage in any activities without regulations on the contents of job. Therefore, changing the status of residence is recommended unless you have special reasons.
On the other hand, it might be better to keep the current status of residence until it expires if the remaining staying period is 2 or 3 years or longer. This is because, in many cases, wife or husband of Japanese is given only 1 year staying period when changing his/her status of residence to Spouse or Child of Japanese National.
By the way, if you would like to engage in the activities that are not permitted to your current status, “Permission to engage in activities other than permitted under the status of residence” is sometimes necessary.
Related Post: Permission to engage in activities other than permitted under the status of residence (ENG. ver. coming soon!)

Summary
- What is Application for Change of Status of Residence?
The procedure necessary to do the activities that are NOT allowed to the current status of residence.
It is the necessary procedure when foreign national residing in Japan changes occupation or status during his/her stay in Japan. - General flow of Application for Change of Status of Residence
STEP1. Preparation and collection of application documents
STEP2. Filling of application documents
STEP3. Examination
STEP4. Result notification from the Agency
STEP5. Reception of renewed resident card - 3 legal requirements for Change of Status of Residence
➊ Conformance with the New Status of Residence
⇒ Related Post: Conformity to Status of Residence and Landing Permission Criteria (ENG. ver. coming soon!)
➋ Good conduct during staying in Japan (“狭義の相当性” in Japanese)
Major items to measure applicant’s conformance with this requirement:
・Applicants must have engaged in activities that are in accordance with the current status of residence.
・Applicants must have good behavior.
・Applicants must have sufficient assets or ability to make an independent living.
・Proper employment and working conditions must be met.
・Tax obligations must be fulfilled.
・Obligations provided by the Immigration Control Act, including notification obligations, must be fulfilled.
*Applicant may be considered NOT to satisfy Requirement② even if all the above items are satisfied.
➌ The application is made based on special unavoidable circumstances
This requirement must be satisfied only when the current status of residence is “Temporary Visitor”. - Application documents according to respective status of residences
The documents to be submitted differ in accordance with the status of residence that applicant want to get.
In this article, document lists for “Engineer/Specialist in Humanities/International Services”, “Student”, and “Spouse of Japanese National/Permanent Resident” are introduced. - Period of time for examination
Standard period of time for procedure of application for change of status of residence is 2 weeks to 1 month. This period is just standard, thus actual period may exceed it. - Timing to make application
Application for change of status of residence must be made after the reason for change is fixed.
Generally, application for change of status of residence is accepted only when remaining period of time until the start of employment contract or entry to school is about 3 months or less. - Penalty
➊ When a foreign national is CLEARLY found to be engaged SOLELY in working activities that are not permitted to the current status of residence (Violation against Immigration Control Act Article70 paragraph(1) item(iv))
– Imprisonment with or without work for not more than 3 years,
– a fine not exceeding 3 million yen, or
– the cumulative imposition of imprisonment with or without work and a fine.
Additionally, who falls under this case also falls under Immigration Control Act Article24 paragraph(1) item(iv) (a), thus he/she may be deported from Japan.
➋ When a foreign national is found to be engaged in working activities that are not permitted to the current status of residence (Violation against Immigration Control Act Article73)
– Imprisonment with or without work for not more than 1 year,
– a fine not exceeding 2 million yen, or
– the cumulative imposition of imprisonment with or without work and a fine
Additionally, who falls under this case also falls under Immigration Control Act Article24 paragraph(1) item(iv) (f), thus he/she may be deported from Japan.
If you have some questions or points to be more deeply explained, please feel free to ask us through the contact form!
Japanese Immigration Column
Columns on Japanese immigration, visa, naturalization, and diplomatic affairs.
- Case Study: Re-application for “Temporary Visitor” visa & Re-application for COE for “Long Term Resident” (vi-A)We, Immigration Lawyer SUGITA International Office, supported re-application for “Temporary Visitor̶ […]
- Customer’s Review: Married couple (India & Vietnam) from Shiga / “Permanent Resident”The clients are married couple (Indian & Vietnamese) living in Shiga prefecture, Japan. Husband was […]
- Customer’s Review:Mr. & Ms. Hiratsuka / Re-marriage without Annulment or Judicial Recognition & COEMs. Hiratsuka once got married and divorced a Japanese man, and she would like to re-marry her current husband […]
- New Service: Low Priced Visa Extension Support / Complete your visa extension application AT YOUR HOUSEToday, we launched new “Visa Extension Applicaition Support” service.You can make visa extension a […]
- Japan to Accept Over 100,000 Foreign StudentsJapan is accelerating acceptance of foreigners, especially foreign students. 150,000 foreign students are waiting to enter Japan, and 100,000 of them are forecasted to enter Japan until end of May 2022.
- Japan Government to Change Upper Limit of Entrance to 10,000/day from April 10On April 1, 2022, Japan Chief Cabinet Secretary Hirokazu Matsuno declared that Japanese government will loose the entrance regulation to change the upper limit from 7,000/day to 10,000/day from April 10.
- Japan Government to Provide Life Support Money and Place for Residence, Chief Cabinet Secretary SaidOn April 1, 2022, Japanese Government held the conference for discussing the acceptance of Ukraine refugees.
- Yokohama-city, Japan, to accept Ukraine RefugeesOn Mar. 8, 2022, Mayor of Yokohama-city, Kanagawa Pref., Japan, declared that Yokohama-city prepared approximately 80 municipal housings for Ukraine refugees.
- Japanese Special Measure “COE Extension” due to Omicron VariantOn Dec. 28, 2021, Immigration Services Agency of Japan has declared the special extension of COE validity due to the impact of omicron variant.
- Sanction “Suspension of Visa Issuance”, Japanese Prime Minister Kishida has announcedOn Feb. 23, 2022, Japanese Prime minister Kishida Fumio announced the sanctions on Russia. The sanctions include the suspension of visa issuance against Russian citizens.
- Japan to increase number of entry up to 7,000/day, Kishida declaredOn Mar. 3, 2022, Japanese Prime Minister Kishida declared that Japan will loosen the regulation of entry of foreigners from 5,000 to 7,000/day.