“Permanent Residence” of Children Born in Japan
Legal requirements / Application instruction / What to do if forgot to make application?
CONTENTS
[Show/Hide]
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Children born in Japan can ACQUIRE “Permanent Residency” in Japan
- 3. Legal Requirements for “Permanent Residency” of Children Born in Japan
- 4. Three Cases where “To Be in the Interest of Japan” Requirement is NOT Satisfied
- 5. Application Flow and Details
- 6. What should you do if application period has passed before you make the application?
- 7. Summary
1. Introduction
As explained in the page of “Permanent Residence in Japan”, the only way to get the status of residence is to change the current status of residence to the one of “Permanent Residence”.
Then, how the children born in Japan, who do NOT have any status of residence on their births, can get the Japanese permanent residency?
The conclusion is that the children born in Japan are specially allowed to apply to ACQUIRE the Japanese permanent residency instead of change of status of residence.
In this article, we provide the detail of the application of permanent residency of children born in Japan.
- What kind of procedure has to be made to get permanent residency of children born in Japan?
- Legal requirements for permission of permanent residency of children born in Japan.
- The cases where children born in Japan can NOT get permanent residency in Japan.
- Documents to be submitted for the application.
- When is the deadline of the application?
=> Jump to the conclusion of this article

2. Children born in Japan can ACQUIRE “Permanent Residency” in Japan

As mentioned above, children born in Japan can ACQUIRE permanent residency instead of change of status of residence.
On the other hand, except for the special cases including “children born in Japan”, foreign nationals can NOT ACQUIRE the permanent residency in Japan. In ordinal cases, the only way for foreign nationals to have status of “Permanent Residence” is to change from their original status of residence that have been given on they enter Japan.
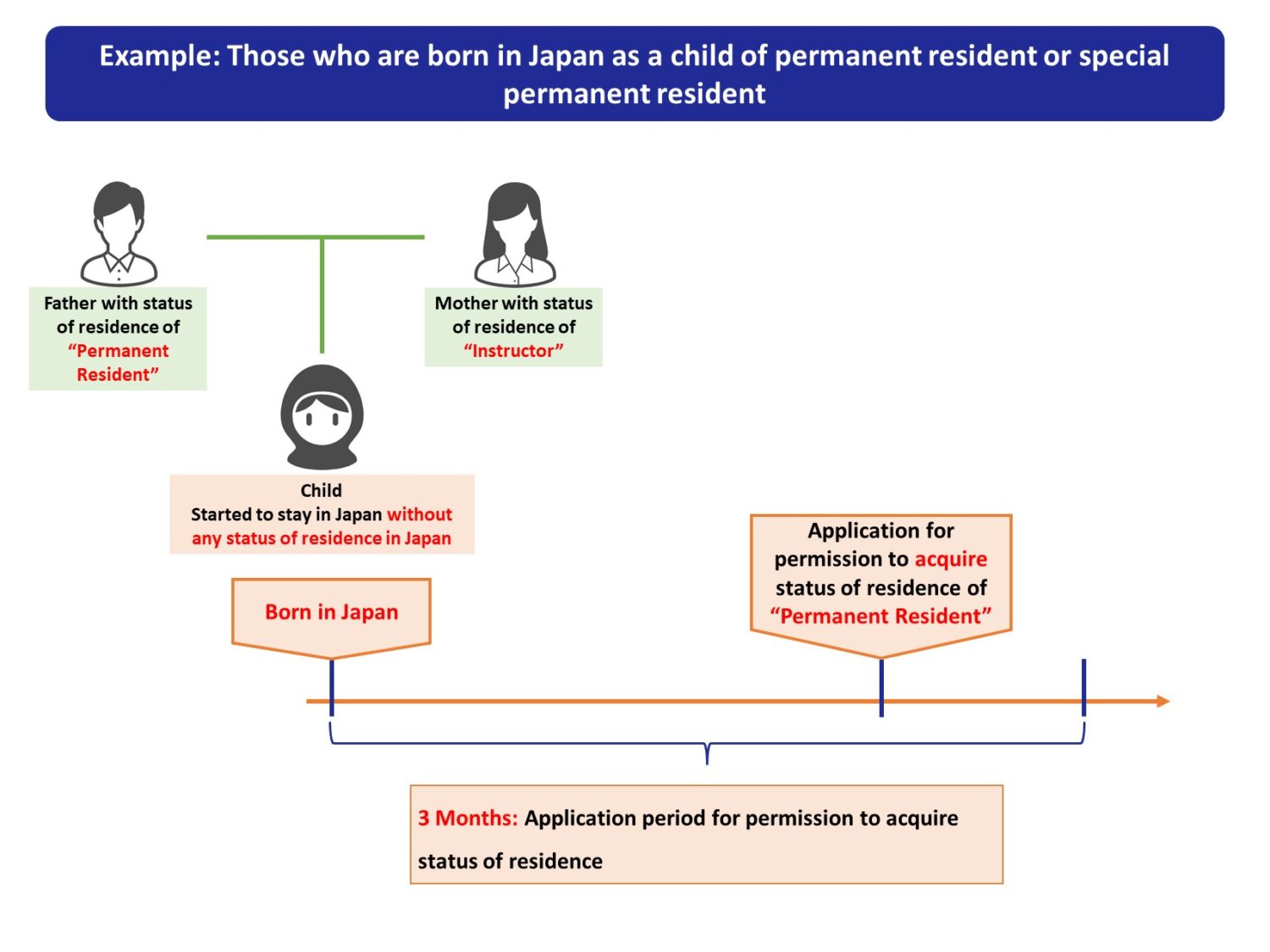
2-1. Definition of “Children Born in Japan”
The detail definition of “Children Born in Japan” is as follows.
Those who are born in Japan as a child of permanent resident or special permanent resident.
The children conforming the above definition do not have any status of residence on their birth. In other words, they do not have original status of residence to change from to the status of “Permanent Residence”.
This is why children born in Japan are specially allowed to apply to ACQUIRE the permanent residency as mentioned above.

3. Legal Requirements for “Permanent Residency” of Children Born in Japan
Legal requirements for “Permanent Residency” of children born in Japan is only “To Be in the Interest of Japan” requirement.
The detail of this requirement is explained in the page of “Legal Requirements of Permission for “Permanent Residence” in Japan”.
“To Be in the Interest of Japan”, in short, requires following items:
- to bring some interest to Japanese society; and
- not to be a burden on Japanese society.
“To Be in the Interest of Japan” requirement is defined detailly in 7 items (a to g), and only those who conform all the 7 items are recognized to satisfy “To Be in the Interest of Japan” requirement.
The 7 items are explained detailly in the below related article.

4. Three Cases where “To Be in the Interest of Japan” Requirement is NOT Satisfied
The permanent residency applications of those who fall under any one of the following items are tend to be denied because of inconformity against “To Be in the Interest of Japan” requirement.
- Any one of the applicant’s parents fall under the condition of deportation and in the middle the deportation procedure.
- Applicant’s supporter is recognized as a burden on Japanese society.
- Applicant’s supporter does not fulfill the public duties.
On the other hand, even if the application is denied for any one of the above mentioned items, this denial can be judged as illegal in some cases.
This is because all of the above items are NOT related to the circumstances of applicant’s self.
This kind of illegal denial is called “他事考慮(Taji-Kouryo)” in Japanese.
Extra Info.
Even if application for permanent residence is denied for any one of the abovementioned 3 items, in some cases, the alternative application for the status of residence of “Spouse or Child of Permanent Resident” might be permitted.

5. Application Flow and Details
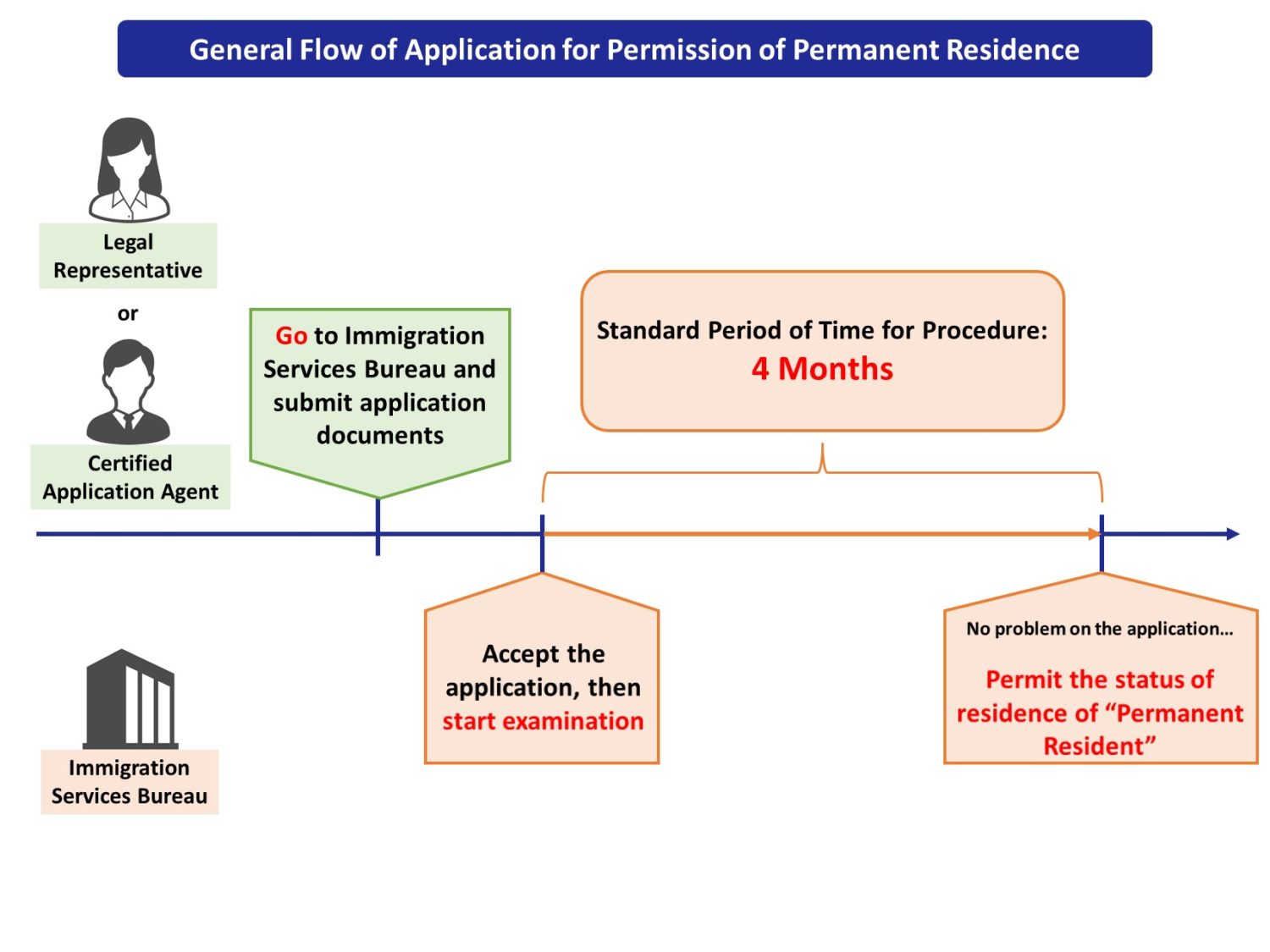
The following chart shows the general flow of application for permanent residence of children born in Japan.
As shown in the chart, applicant must be present at Immigration Services Bureau to submit application documents.
In principle, applicant him-/herself must go to Immigration Office, however, legal representative (such as applicant’s parents) and certified agent (called “Shinsei-Toritsugi-Sha” in Japanese) are also allowed to go to Immigration office and submit the documents.
5-1. Documents

- Application sheet for permanent residence
=> (External link: Application format) - Document certifying identity of applicant
(1) In case applicant is child of Japanese parent: Copy of the family register of Japanese parent
(2) In case applicant is child of permanent resident of special permanent resident: Any one of the following documents that certifies the parent-child relationship of applicant and his/her parent
a. Birth certificate
b. The document equivalent to birth certificate that certifies the parent-child relationship of applicant and his/her parent - Copy of certificate of residence that includes information of applicant and all his/her family members (“Jumin-hyou” in Japanese)
- Any one of the following documents that certify the occupation of applicant’s supporter
(1) In case the supporter is employed by any party such as company: Certificate of employment
(2) In case the supporter is self-employed: All the following documents
a. Copy of tax return
b. Copy of business permit
(3) Other cases: Document explaining supporter’s occupation (free format) and its proof material - Document proving supporter’s income and tax payment status in latest 1 year
(1) Document proving payment status of resident tax
a. Taxation (or tax exemption) certificate and tax payment certificate of resident tax in latest 1 year (the certificate must show supporter’s annual gross income and tax payment status)
b. Document proving that the supporter has payed resident tax in the appropriate period in latest 1 year (such as copy of passbook, or receipt)
(2) Document to check the payment status of national tax
Withholding tax, Special Income Tax for Reconstruction, self-declared income tax, consumption tax, local consumption tax, inheritance tax, and No. 3 tax certificates
(3) Others: Any one of the following documents that proves supporter’s income
a. Copy of passbook
b. Equivalent document of copy of passbook - Document proving supporter’s payment status of fees of public pension and public medical insurance
(1) Document proving the payment status of fee of public pension in latest 1 year
a. Pension service letter (Nenkin Teiki-bin) (All the history of payment shall be shown on)
b. Printed copy of the monthly pension record page of “NENKIN NET” (personal online account service for pension in Japan)
c. Copy of the receipt of national pension fee
* Applicants shall submit one or more documents of above a to c in accordance with his/her circumstance.
(2) Document proving payment status of public medical insurance fee in latest 1 year
a. Copy of health insurance card
b. Copy of national health insurance card
c. Payment certificate of fee of national health insurance
d. Copy of receipt of national health insurance fee - Passport of applicant (only showing, not submitting)
- Document on sponsorship
(1) Declaration of sponsorship
=>(External link: Format)
(2) Following documents on sponsorship
a. Document proving sponsor’s occupation: Certificate of employment (in case of employee), Copy of company register (in case of company director)
b. Document proving sponsor’s income in latest 1 year (such as taxation certificate of resident tax, or copy of withholding tax)
c. Certificate of residence (“Jumin-hyou” in Japanese) - Written oath on permanent residency
=>(External link: Format)
Extra Info.
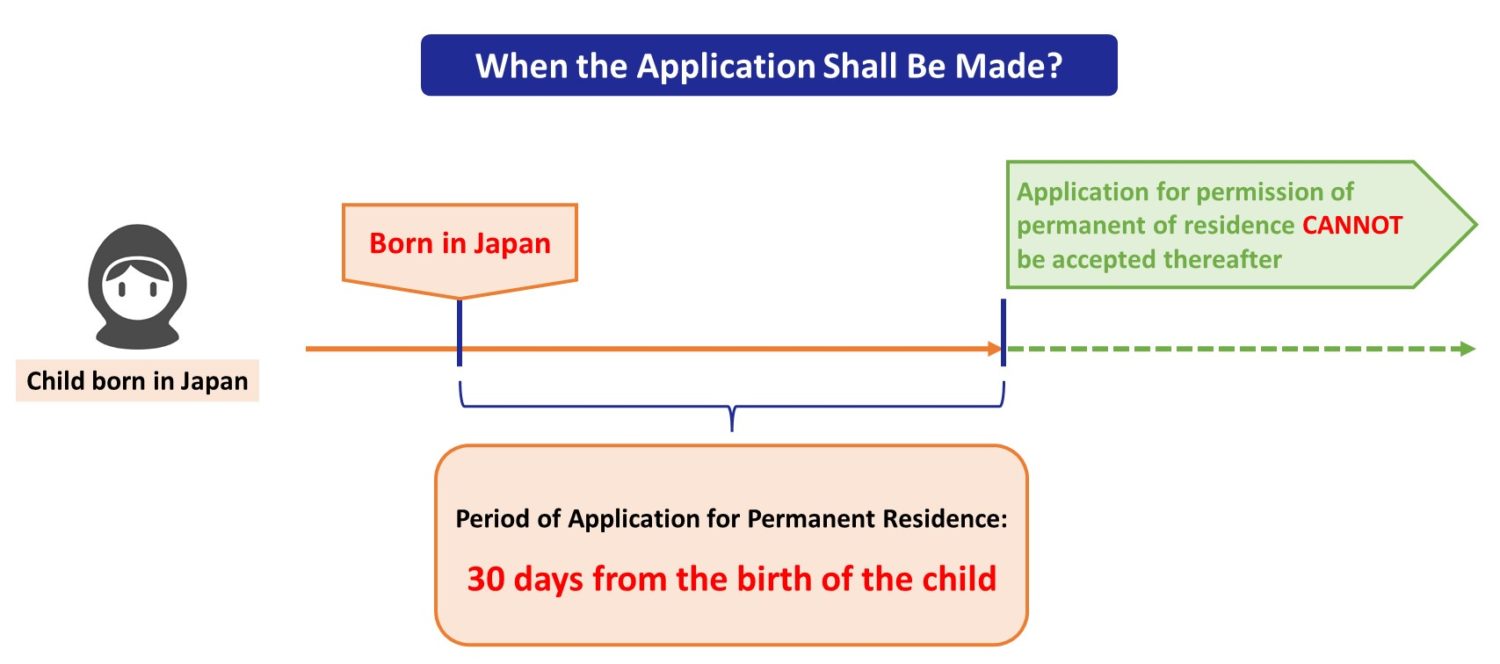
Application of permanent residence of children born in Japan must be made within 30 days from their birth (details of application period are explained in Sec. 6).
In case passport of the child cannot be issued within this period, applicant can submit any one of the following documents instead of passport:
・Birth certificate issued by the government of the nation where the applicant has a nationality; or
・Proof of birth registration issued by Japanese government.
Extra Info.
Applicant younger than 16 years old does not have to submit photograph although it is normally required in application of permanent residence.
This is that, children born in Japan does not have to submit their photos for the application of permanent residence.
5-2. Standard Period of Time until Permission

As of January, 2022, Immigration Services Agency of Japan says that standard period of time until permission of permanent residence is 4 months after the application is made.
Standard period of time is the time that an authority normally takes before it makes any reactions, permission or denial, to an application.
Extra Info.
Standard period of time is just a “Standard”, thus Japanese authorities do not have to comply with it.
In other words, even if standard period of time is officially announced, more time might be required in the practical procedure.
5-3. When the Application Shall Be Made?
The application of permanent residence of children born in Japan must be made within 30 days from their birth.
In case the application is not made within this period, the applicant can NOT get the status of residence of “Permanent Resident” on his/her birth.
However, even in this case, the children born in Japan can continue to stay in Japan by taking other procedures.
The specific information of other procedures are explained in the next section.

6. What should you do if application period has passed before you make the application?
As mentioned above, children born in Japan can continue to stay in Japan by taking other procedures even if application for permanent residence has not made within the application period.
In this case, the applicant can take any one of the following 3 procedures in accordance with the length of the passed period from the child’s birth.
① Within 60 days from the birth of child
If 30 days have passed since the birth of child, the application for permanent residence, in principle, can NOT be accepted by the Immigration Services Bureau.
In this case, the application for the status of residence of “Spouse or Child of Permanent Resident” might be accepted within 60 days from the birth of child.
The child with the status of residence of “Spouse or Child of Permanent Resident” can make the application for changing his/her status of residence to “Permanent Resident” after he/she has continuously lived in Japan to satisfy “Continuous Stay Requirement”.
Therefore, status of residence of “Permanent Resident” can be given to the child, although it takes long time, in case 60 days have NOT passed since the birth of child.
Extra Info.
Those who are born in Japan as a child of permanent resident or special permanent resident is subject to “Exception of 10-years continuous residence in Japan on Permanent Residence Application”.
More specifically, if those people continuously stay in Japan for only 1 year, they are recognized to satisfy “Continuous Stay Requirement”.
External link: “Guideline for permission for permanent residence”
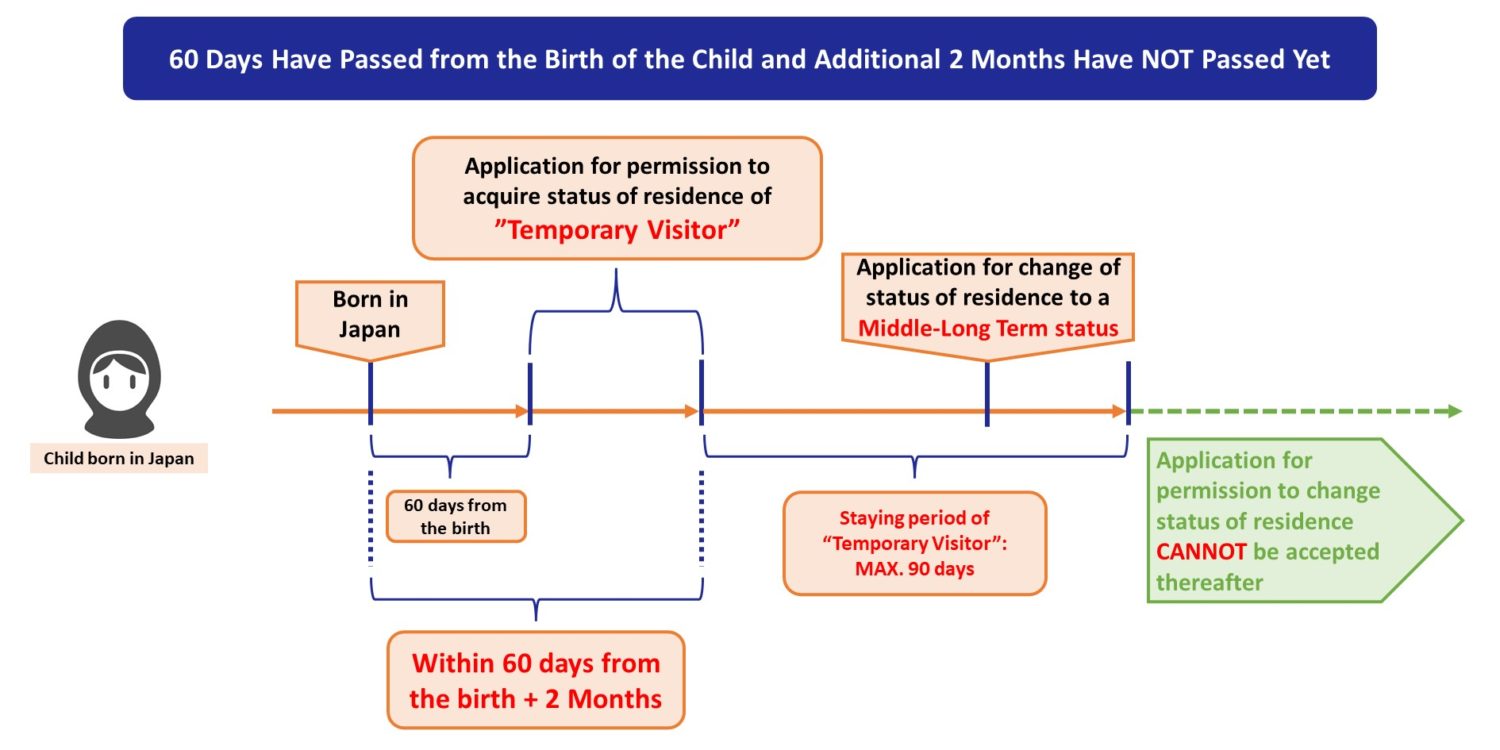
② 60 days have passed from the birth of child and additional 2 months have NOT passed yet
If 60 days have passed since the birth of child, the applications for both permanent residence and “Spouse or Child of Permanent Resident”, in principle, can NOT be accepted by the Immigration Services Bureau.
In this case, only when the applicant satisfy all the following 4 conditions, the application for the status of residence of “Temporary Visitor” can be accepted by the Immigration Services Bureau.
- Additional 2 months have NOT passed yet after 60 days from the birth of the child;
- The applicant does NOT fall under any conditions of deportation;
- The authority admits that elapsing of the application period without application is recognized to be within reason; and
- The authority admits that the application would have been permitted if the application had been made within the application period.
The child can continue to stay in Japan by changing the status of residence from “Temporary Visitor” to any one of the middle-long term statuses of residence.
Same as ①, “Exception of 10-years continuous residence in Japan on Permanent Residence Application” is applied also in this case.
Extra Info.
In this case, the child can NOT directly change the status of residence from “Temporary Visitor” to “Permanent Resident”.
This is because 1 year or longer stay is required to satisfy “Continuous Stay Requirement” and the staying period permitted to “Temporary Visitor” is, even at longest, only 90 days.
Therefore, in this case, the child firstly has to change the status of residence from “Temporary Visitor” to middle-long term one, then finally can make the application for permission to change the status of residence to “Permanent Resident”.
③ 60 days have passed from the birth of child and additional 2 months have ALREADY passed
In case 60 days have passed from the birth of child and additional 2 months have already passed, in principle, the child born in Japan can no longer stay in Japan.
In this case, deportation procedure is taken.
Extra Info.
In some cases, mother with foreign nationality and father with Japanese nationality are contending in court for legitimacy and parent-child relationship between the father and the child (applicant) on the birth of the child.
In this kind of cases, it is impossible to treat the child as either:
① a child of Japanese; or
② a child of a foreign national
until the case is closed.
If the child is above ①, the procedure to take is registration of birth as a child with Japanese nationality. On the other hand, if the child is above ②, the procedure to take is application for permission to acquire status or residence. That is, which procedure to take cannot be decided until the case is closed.
Therefore, the timing where the case is closed is sometimes considered as the start point of application period by Immigration Services Bureau. In this case, the applicant is allowed to make an application within 30 days from this starting point.

7. Summary
- What kind of procedure has to be made to get permanent residency of children born in Japan?
Application for permission to acquire status of residence of “Permanent Resident”.
(NOT application for permission to change status of residence) - Legal requirements for permission of permanent residency of children born in Japan.
Only “To Be in the Interest of Japan” requirement. - The cases where children born in Japan can NOT get permanent residency in Japan.
・Any one of the applicant’s parents fall under the condition of deportation and in the middle the deportation procedure.
・Applicant’s supporter is recognized as a burden on Japanese society.
・Applicant’s supporter does not fulfill the public duties. - Documents to be submitted for the application.
➊ Application sheet for permanent residence
➋ Document certifying identity of applicant
➌ Copy of certificate of residence that includes information of applicant and all his/her family members (“Jumin-hyou” in Japanese)
➍ Document that certifies the occupation of applicant’s supporter
➎ Document proving supporter’s income and tax payment status in latest 1 year
➏ Document proving supporter’s payment status of fees of public pension and public medical insurance
➐ Passport of applicant (only showing, not submitting)
➑ Document on sponsorship
➒ Written oath on permanent residency - When is the deadline of the application?
Within 30 days from the birth of the child. However, even if this period has passed without making the application, there is another way to acquire the status of residence of “Permanent Resident”.
If you have some questions or points to be more deeply explained, please feel free to ask us through the contact form!
Japanese Immigration Column
Columns on Japanese immigration, visa, naturalization, and diplomatic affairs.
- Case Study: Re-application for “Temporary Visitor” visa & Re-application for COE for “Long Term Resident” (vi-A)We, Immigration Lawyer SUGITA International Office, supported re-application for “Temporary Visitor̶ […]
- Customer’s Review: Married couple (India & Vietnam) from Shiga / “Permanent Resident”The clients are married couple (Indian & Vietnamese) living in Shiga prefecture, Japan. Husband was […]
- Customer’s Review:Mr. & Ms. Hiratsuka / Re-marriage without Annulment or Judicial Recognition & COEMs. Hiratsuka once got married and divorced a Japanese man, and she would like to re-marry her current husband […]
- New Service: Low Priced Visa Extension Support / Complete your visa extension application AT YOUR HOUSEToday, we launched new “Visa Extension Applicaition Support” service.You can make visa extension a […]
- Japan to Accept Over 100,000 Foreign StudentsJapan is accelerating acceptance of foreigners, especially foreign students. 150,000 foreign students are waiting to enter Japan, and 100,000 of them are forecasted to enter Japan until end of May 2022.
- Japan Government to Change Upper Limit of Entrance to 10,000/day from April 10On April 1, 2022, Japan Chief Cabinet Secretary Hirokazu Matsuno declared that Japanese government will loose the entrance regulation to change the upper limit from 7,000/day to 10,000/day from April 10.
- Japan Government to Provide Life Support Money and Place for Residence, Chief Cabinet Secretary SaidOn April 1, 2022, Japanese Government held the conference for discussing the acceptance of Ukraine refugees.
- Yokohama-city, Japan, to accept Ukraine RefugeesOn Mar. 8, 2022, Mayor of Yokohama-city, Kanagawa Pref., Japan, declared that Yokohama-city prepared approximately 80 municipal housings for Ukraine refugees.
- Japanese Special Measure “COE Extension” due to Omicron VariantOn Dec. 28, 2021, Immigration Services Agency of Japan has declared the special extension of COE validity due to the impact of omicron variant.
- Sanction “Suspension of Visa Issuance”, Japanese Prime Minister Kishida has announcedOn Feb. 23, 2022, Japanese Prime minister Kishida Fumio announced the sanctions on Russia. The sanctions include the suspension of visa issuance against Russian citizens.
- Japan to increase number of entry up to 7,000/day, Kishida declaredOn Mar. 3, 2022, Japanese Prime Minister Kishida declared that Japan will loosen the regulation of entry of foreigners from 5,000 to 7,000/day.